PROGRAMMING GRADE 11
(PROG-111) WEEK 11-20
Question text
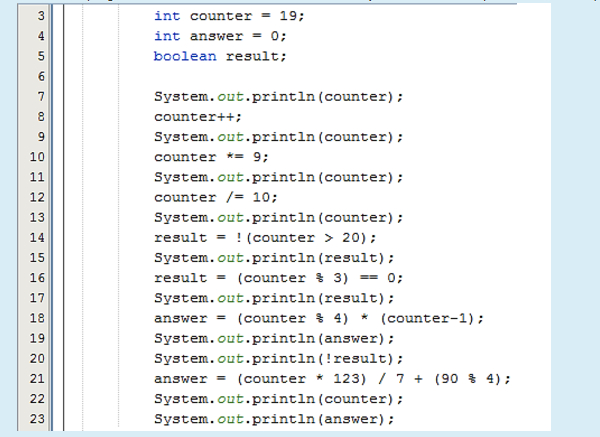
Observe the following statements and decide whether the variable result’s value is TRUE or FALSE.
Given that:
int x = -77;
int z = 43;
result = (z < x && 1 != 10) ? true : false;
result = (z != 43) ? true : false;
Select one:
False
Question text
Read each statement carefully and decide whether it’s TRUE or FALSE.
The last line of code, with a close brace { symbol, is properly indented.
Select one:
False
Question text
True or False: Brackets [] are also separators used in declaring arrays.
Answer:
True
Question text
Refer to the block of codes below. Read each statement carefully and decide whether it’s TRUE or FALSE.
There is an error in line 9.
Answer:
TRUE
Question text
True or False: Operators, in Java programming language, use special symbols to call methods and their objects.
Answer:
False
Question text
Read each statement carefully and decide whether it’s TRUE or FALSE.
There are no errors in the program.
Select one:
False
Question text
Refer to the block of codes below. Read each statement carefully and decide whether it’s TRUE or FALSE.
Line 9 uses a traditional comment which uses double forward slash.
Answer: False
Question text
True or False: Many programmers can be literate with Java programming language for it is intended to be that way.
Answer:
True
Question text
True or False: You’ll know there’s an error if you see a red circle with an exclamation point in Netbeans IDE.
Answer:
True
Question text
Observe the following statements and decide whether the variable result’s value is TRUE or FALSE.
Given that:
int x = -77;
int z = 43;
result = (z < x && 1 != 10) ? true : false;
result = (x = 100) >= z;
Select one:
True
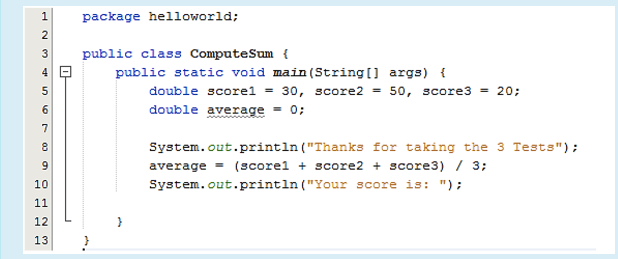
The file is accurately named – Students.java.
-false
There are three (3) separators found in line 13.
-FALSE
There is an error in line 9.
-True
result = 90 < x || -1 < z;
-True
The last line of code, with a close brace { symbol, is properly indented.
-False
Assuming there are no errors in the code, line 13 would display When I graduate, I’d be 18.
-True
Figure 2 shows the Netbeans Integrated Development Environment.
-True
The last line of code will output 100.0.
-True
True or False: An exclamation point in Java means NOT. Therefore, != means not equal to.
-True
There are two types of comments used in the program above – end of line and Javadoc comments.
-True
result = (z < x && 1 != 10) ? true : false;
-False
There are keywords found in line 7.
-True
In line 11, the value of personage is 18.
-TRUE
If there are no errors in the program, the first line of output would read Hi, I’m a normal person.
-False
result = (x * z + (z += 7)) >= 100;
-False
True or False: Logical OR operator will result to false if one of the expressions is false.
-False
True or False: Semicolon (;) is a separator used to end a Java statement.
-True
True or False: There are five types of integer data types – byte, short, int, long and float.
-False
True or False: Single equal sign (=) is used for assigning values while double equal sign (==) is used in comparing values.
-True
True or False: Java’s ternary operator is a short hand for the if-then-else statement which uses a question mark and a colon.
-True
True or False: JDK or Java Design Kit is required to compile and run Java apps and applets.
-True
On line 6, average is equal to 0. But on line 9, average will be equal to 100.
-False
True or False: Identifiers in Java are, in simple words, name that you give to Java class, variables and methods.
-True
True or False: When you run javac in a command line interface, it will automatically create another file with a filename extension .class.
-True
Line 9 uses a traditional comment which uses double forward slash.
-FALSE
There are five (5) separators used in line 8.
-TRUE
There are no errors on line 8.
-FALSE
True or False: Syntax is basically the spelling and grammar errors compiled in a Java programming language. It should be avoided in writing apps and applets.
-False
True or False: Operators, in Java programming language, use special symbols to call methods and their objects.
-False
If you run this program, the second line of output will read Your score is:.
-True
True or False: Java is a low level programming language.
-False
There are also punctuators used in line 10, in between System, out and println, the parentheses and semicolon.
-TRUE
If there are no errors and this simple program runs through CLI, the first line will display: Hi, students!
-False
True or False: Brackets [] are also separators used in declaring arrays.
-True
Substrings can contain 1 or 2 arguments.
-true
Determine the output.
-bar
The index of the letter “y” in string “Doggy” is 5.
-False
Determine the output.
-foo
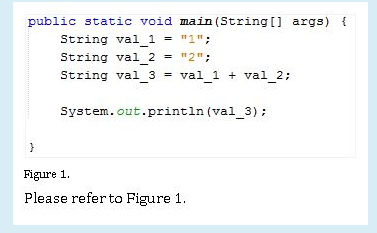
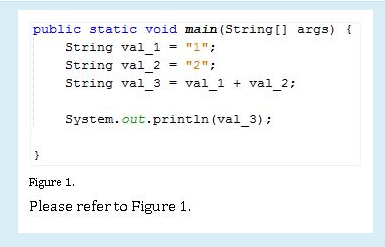
TRUE OR FALSE: The value “val_3” is a white space “ “.
-False
True or False: Variable 1st_num is a good variable name in Java programming.
-False
TRUE OR FALSE: “val_2” contains “The”
-True
True or False: Instance variables are declared inside a method but outside a class.
-False
True or False: Variable names in Java are not necessarily case sensitive.
-False
Determine the output
-36
True or False: Public, private and protected are some of the return types used in Java programming.
-False
True or False: Divide and conquer strategy, in programming, is also known as the top-down design.
-True
If there are no errors in the program, line 9 would display I weigh 160.
-False
True or False: A boolean variable can only have two values; it is either true or false.
-True
result = !((x * 10) < z);
-False
result = -(-z) == 43;
-True
True or False: If you get an error while running the javac command in the CLI, it could be resolved by editing the Path value in Environment Variables.
-True
True or False: The subtraction assignment operator subtracts the left and right operand and assigns the difference to the operand at the right.
-False
x += x;
result = x == 154;
-False
The second line of output will be: You are in Year 11.
-True
True or False: The conditional AND operator uses two ampersand (&&) symbols.
-True
result = 43 <= z;
-True
True or False: You’ll know that a variable is a class variable when you see that variable inside a class with the word static.
-True
The string method “length( )” returns the number of characters within a string.
-True
A string can contain numbers.
-True
TRUE OR FALSE: This is an example of concatenation.
-True
TRUE OR FALSE: The value of “val_4” is “fox”
-False
TRUE OR FALSE: “val_2” contains “The”.
-True
Determine the output.
-f6
Languages which use procedural programming include C, (Answer) FORTRAN, Pascal and BASIC.
-C++
True or False: Local variables are declared inside the default method.
-False
Strings can be declared with str.
-False
True or False: Procedural programming involves instructing the system as to how to complete a task.
-True
TRUE OR FALSE: The output of this code is “The quick brown fox”
-False
Among the expressions below which is a statement?
-True
Expressions can be long and complex.
-true
number++; is an expression
-true
For-loops has a set number of iterations before starting.
-True
The equals( ) method can compare more than 2 arrays.
-False
While loops can use Booleans at test expressions.
-True
The test expression of the if statement is _______
-less than or equal to
There are four (4) major features of an object-oriented programming language – encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism and abstraction.
-True
Using a break; statement causes the loop to jump to the next iteration.
-False
x+1 is example of a statement.
-False
number++; is a block
-False
Arrays are
-Objects
The operator “new” allocates a memory block the size of what is declared.
-true
A class block can be an expression
-False
Statements can be expressions.
-False
Integer arrays can be populated with characters.
-False
Declaration clauses are declared as “number + 1”.
-False
Loops can be stopped with a break; statement.
-True
The equivalent of Paragraphs in coding is?
-Expressions
If statements cannot be nested in switches
-true
The length( ) method returns the size (number of indices) has.
-True
When polymorphism is used, the Java object can only take one form. Subclasses should have the same function with the parent class.
-False
Arrays can contain (Answer) number of elements.
-Any
“||” and “&&” can be used in conditional statements.
-True
A class statement has three (3) major parts – declaration, initialization and instantiation.
-False
Declaring an object in Java uses the new keyword to create a new object.
-False
Please refer to Figure 2 to answer the question below: If the expression “num = 0” is changed to “num = 5” the final output will be
-5
Expressions can be statements.
-True
Blocks can contain more blocks of code.
-True
If-else statements can be nested in?
-All of the choices
Statements are equivalent to paragraphs.
-False
A (answer) array is an array containing true or false values.
-boolean
Switches are always used with if-else statements
-False
True or False: The modulus operator returns the remainder of a division operation instead of the quotient.
-true
Determine the output.
String val_1 = “564298”;
-5698
Determine the output.
String val_1 = “35”;
-4
The return value of the length( ) method is an integer
-true
A superclass is also known as a parent class.
-true
For-loops can be nested in while loops.
-true
In instantiating an object, the keyword instance is used.
-False
Object oriented programming utilizes the top down method
-False
Expressions are like clauses.
-true
The sort( ) method is always ascending.
-true
Arrays are data types.
-False
Variables must be declared as (Answer) for it to be fully hidden.
-private
While statements check the test expression at the end.
-False
The else statement can be used alone.
-False
The fill( ) method (Answer) the array with specific values.
-Fills
The output of println is
-55555
The person’s weight is declared correctly with the correct data type (byte) and value (160).
-FALSE
Determine the output.
String val_1 = “foo”
String val_2 = “bar”
val_2 = val_1;
val_1 = val_3;
System.out.println(val_1);
-bar
Determine the output.
String val_1 = “foo”
String val_2 = “bar”
val_2 = val_1;
val_1 = val_3;
System.out.println(val_2);
-foo
Switches can work properly even without the “break” expression.
-True
Blocks can be one liner or huge classes.
-True
The test expressions in conditional statements can be left empty.
-False
Abstraction works by hiding the implementation details and showing only the functions necessary.
-True
A single array can hold multiple data types
-False
A polymorphic object can pass more than one Is-a test.
-True
Another loop can be used as test expression.
-False
True or False: Public, static and void are sample of Java reserved keywords.
-True
The value of “pStr” in line 24 is
-True
The default syntax of a constructor is <class_name>(parameter, parameter){ }
-False
A nested class is not an inner class.
-False
Nested classes causes them to become abstracted
-False
A nested class is also called
-inner class
If you want some variables and methods hidden from other classes, you could implement encapsulation where these variables and methods are wrapped in a single unit.
-True
A constructor can only have 1-2 overloads or parameters.
-False
All possible data types of an array can be retuned as a string by the toString( ) method.
-True
Abstracted classes can contain 1 or more abstract methods.
-True
Abstraction shows the every bit of detail and implementation on how an application does something.
-False
Initialization is a process where the constructor is called for.
-True
The default syntax of a constructor is <class_name>( ){ }
-True
Classes cannot be nested.
-False
Abstract classes cannot have nested classes.
-False
The parent class of a nested class is called an outer class
-True
An inner class can be constructed directly without reference to the outer class.
-False
Arrays can be read backwards
-True
A single array can hold
-One data type
Abstracted methods already have implementations inside.
-False
are special methods to initialize objects.
-constructors
Constructors have 3 basic rules to follow.
-False
Nesting classes increases encapsulation.
-True
Each index can only contain (Answer) element.
-one
The sort( ) method can be set to sort only a part of an array.
-False
Subclasses or child classes could have different behaviors but still share the same functions from their parent class.
-True
Abstract methods must have an explicit return value
-False
An abstract class must not contain abstract methods.
-False
Abstracted classes can be nested.
-True
A subclass constructor cannot invoke a superclass constructor.
-False
A class acquiring fields and methods of another class is called inheritance.
-True
Parallelsorting utilizes
-More cpu processing cores
method can copy one array to another.
-arraycopy()
Conditional test expressions can contain declarations
-True
A child class inherits all the methods of every other class.
-False
f the value of “pStr” in line 7 is changed to _______ then the value of “pStr” in line 24 will be changed as well.
-True
The type of loop that checks the test expression at the end.
-do-while
An array of integers should be declared as
-int[]
A class which contains the abstract keyword in its declaration is known as an
-abstract class
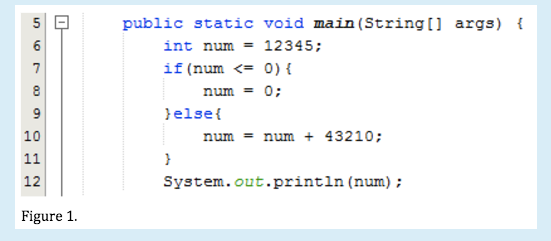
Please refer to figure 1 to answer the question below: In figure 1 if(x==5) is
-skipped
The first line of the code should have either a yes or no value.
-False
Determine the output.
String val_1 = “25”;
String val_2 = “80”;
-200
What does ‘new’ in int[ ] myArray = new int[n] do?
-Assigns memory for the array
is also known as a parent class.
-Super class
Determine the output.
String val_1 = “foobar”;
String val_2 = “”;
-boar
Polymorphic objects can pass (answer) Is-a test.
-More than one
True or False: Traditional comments start with /** (forward slash and two asterisks) and ends with */ (asterisk and forward slash).
-False
True or False: Netbeans is one of the IDEs or Integrated Development Environment to run Java programs.
-True
For-loops can check the test expression at the end.
-False
Polymorphism is the ability of a Java object to take
-Directly
Constructors can have
-any number
When the program runs, and assuming there are no errors, its first line will be begin printing.
-FALSE
Which of these is a proper decrement?
-x-10;
All are methods of the array class except
-substring()
The error in Figure 2 is
-“tralse”;
A constructor (answer) contain an explicit return type
-cannot
Abstracted methods need (answer) for implementations.
-sub-classes
Line 14 will yield an error. It will be corrected if you place */ after the method.
-FALSE
The name of a constructor must be (answer) as your class.
-same
The limit of dimensions an array can have without errors is
-255
This type of declaration is discouraged.
-String myArray[ ];
The following figure shows the Netbeans Integrated Development Environment.
-True
The equivalent of clauses in coding is?
-Expressions
Int num = 1; for(num=num;num<=10;num++) is an acceptable code snippet.
-true
Loop that has a pre-determined number of iterations
-while
An int can be used even if it is declared outside a for-loop.
-true
Overload methods must be the same name as the class
-true
What the break statement in this example does is ________.
-Ends the whole instance of the loop
The random( ) method sorts the array randomly.
-False
The last part in a for loop setup can be an ________.
- both
The “1” in arrayName[1] is called an ________.
-Index
The continue; statement ends all the iterations of a loop.
- False
Which is not a proper increment?
- n+-;
Infine for-loops can be declared as for( ){ }.
- False
If-if is more logical than else-if.
- False
The else statement can be removed if not needed.
-True
Expressions, Statements and Blocks are like composing sentences and paragraphs.
-True
You can declare a new method in the subclass which is not declared in the superclass.
-True
The return value of the equals( ) method is ________ .
-None of the choices
The Arrays.sort( ) method sorts an array into _________ order.
-Ascending
This type of declaration is discouraged: “int myArray[ ]”
- True
An if-else-if-else statement is a block.
-True
If the increment num=num+2 is changed to num++, the final value of num will be ________.
- 5
The term of each pass through a loop makes is called?
-iteration
Loops must always have a continue or break statement.
-False
1+2+3/4*5 is an unambiguous expression
-False
Conditional statements can contain more conditional statements.
- True
int num = 1;
if(num==1 && num<=1){
body;
}
The conditional statement will _______.
- execute the body
byte( ][ ][ ) myArray; is an example of ________.
- An error
An array _______ hold objects.
- can
A reference variable can be reassigned to other objects provided that it is not declared ________.
- final
The test expression of conditional statement cannot contain _______
- !
Each pass through of a loop is called a cycle.
- True
If the increment “num = num + 2” is changed to “num = num + 1” the final output will be _______.
- 0
Ifs and else-ifs test expressions return true or false.
- True
_______ classes increase the encapsulation of you methods and data.
- nesting
Constructed methods are initialized with 0 or null depending on the data type.
- true
The else statement catches whatever argument the if and else-if didn’t
- True
An iteration of a loop is equivalent to one pass through.
- true
38. If we change the initial value of num in line 6 to “num = 0”, the println output will be _______
- 0
The else-if statement can be used alone.
- false
Abstract methods need sub-classes to contain their implementations.
-true
The method arraycopy( ) does what?
- Copies the contents of an array to a destination array.
An array can be infinitely long.
- False
A loop can contain no expressions or statements inside.
- true
Conditional statements are the same as declaration statements.
- False
You cannot use inherited methods directly in a child class.
- False
The equals( ) method compares 2 arrays.
- True
Method invocations are statements
- True
To implement encapsulation, you have to declare class variables with the private modifier.
- True
Inner class methods can be called by constructing the inner class.
- False
Encapsulated data are hidden from other classes.
- True
Refer to the code snippet below. Identify what part of a method is shown in each number (the underlined one).
GIVEN: public int getArea
Answer: Method Name
Fill in the blanks with the correct answer.
Answer: val_1 + val_2
Read each statement carefully and decide whether it’s TRUE or FALSE.
The filename of the Java file above is computesum.java.
Answer: False
Refer to the code snippet below. Identify what part of a method is shown in each number (the underlined one).
GIVEN: int getArea
Answer: Return Type
Fill in the blank:
Answer: foo
Procedural programming will be tricky for applications.
Answer: small
Strings can directly concatenated to an int.
Answer: False
TRUE OR FALSE: The value of “val_3” is 3
Answer: FALSE
Fill in the blank:
Answer: barfoo
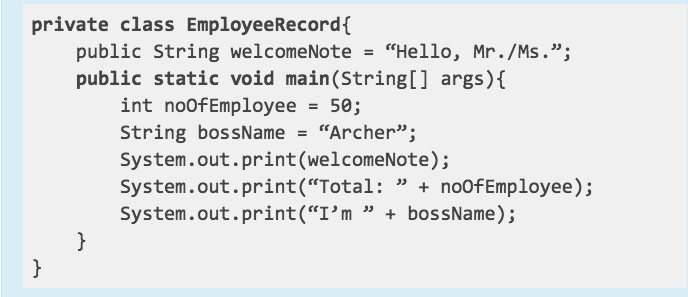
Refer to the code snippet below. Determine whether the given is a local variable, instance variable, access modifier or a class name.
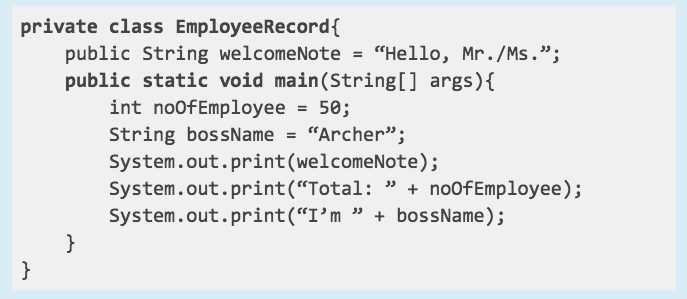
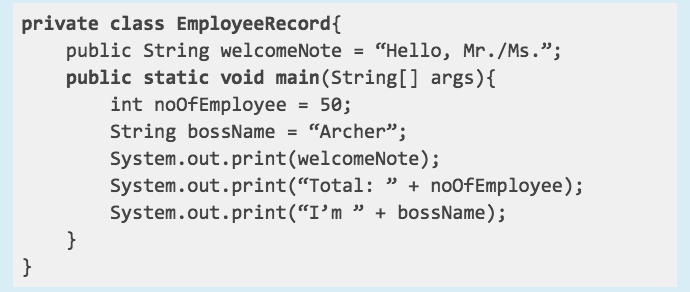
GIVEN: private class EmployeeRecord
Answer: access modifier
TRUE OR FALSE: The assigned values of “val_1” & “val_2” are integers.
Answer: FALSE
Fill in the blank:
Answer: 200
True or False: A method could be declared without any parameters.
Answer: False
Fill in the blank:
Answer: foo
Refer to the block of codes below. Read each statement carefully and decide whether it’s TRUE or FALSE.
There are no errors in line 11.
Answer: TRUE
Determine the output.
Answer: error
True or False: Non-procedural programming focuses on how a task is done rather than on what task should be done.
Answer: False
Refer to the code snippet below. Determine whether the given is a local variable, instance variable, access modifier or a class name.
GIVEN: private class EmployeeRecord
Answer: class name
Determine the output.
Answer: chocolate bar
True or False: If you are running a program through CLI, the class name and the file name should be different.
Answer: False
Fill in the blank:
Answer: 6
The “indexOf( )” method returns the first instance of the specified character.
Answer: True
Please refer to figure 1 to answer the question below:
If we change the initial value of num in line 6 to “num = 0”, the println output will be
Answer: 0
Strings can readily accept int values.
Answer: True
True or False: Keywords are Java reserved words which are used as identifier for interface, constants and constructs.
Answer: True
Refer to the code snippet below. Determine whether the given is a local variable, instance variable, access modifier or a class name.
GIVEN: int noOfEmployee
Answer: local variable
True or False: After compiling a Java program through the CLI, run it using the java and press Enter.
Answer: True
Refer to the program below. Read each statement carefully and write the output for each line specified.
Line 22 will display on the screen.
Answer: 1